Did you just get bitten by the road bike bug? Did you watch Tour de France: Unchained and feel hungry for more? Or have you always been puzzled by the daily deluge of Tour de France news? Then this beginner’s guide is for you.
We’ll cover the fundamentals of how this “game” is played. Also, we’ll delve into cycling’s paradoxical balance between being simultaneously a team sport and an individual sport, and many ways riders and teams play to win.
If you’re a seasoned cycling fan, please feel free to share this with your curious in-laws who always email you questions about pelotons, yellow jerseys, and more. We’ve all been there before!
[button]Shop road bikes[/button]
How The Tour de France Works
The Tour de France: Infographic

What is the Tour de France
- The Tour de France is the world's most prestigious bike race which has been running for over 100 years.
- The Tour takes riders all across France, through the Alps and the Pyranees, and finishes in Paris.
- This year it will take place: July 1 - July 23, 2023
- The total race distance this year: 3,404 Km / 2,115 Mi
- The Grand Départ - The Tour de France often starts somewhere outside of France so other cities and countries can experience the excitement of the Tour. This year, the Tour will start in Bilbao, Spain.
Key Details
- 22 pro cycling teams will compete with 8 riders each (176 riders total)
- The race is split into 21 stages
- Riders race 1 stage per day
- Each stage has a stage winner. Winning a single stage at the Tour is a big deal.
- On average, racers will ride over 100 miles per stage.
- Riders will get 2 rest days, one after the first week, and another after the second week.
- The overall winner of the Tour de France is the rider with the fastest time after all 21 stages.
How To Win The Tour de France - Yellow Jersey
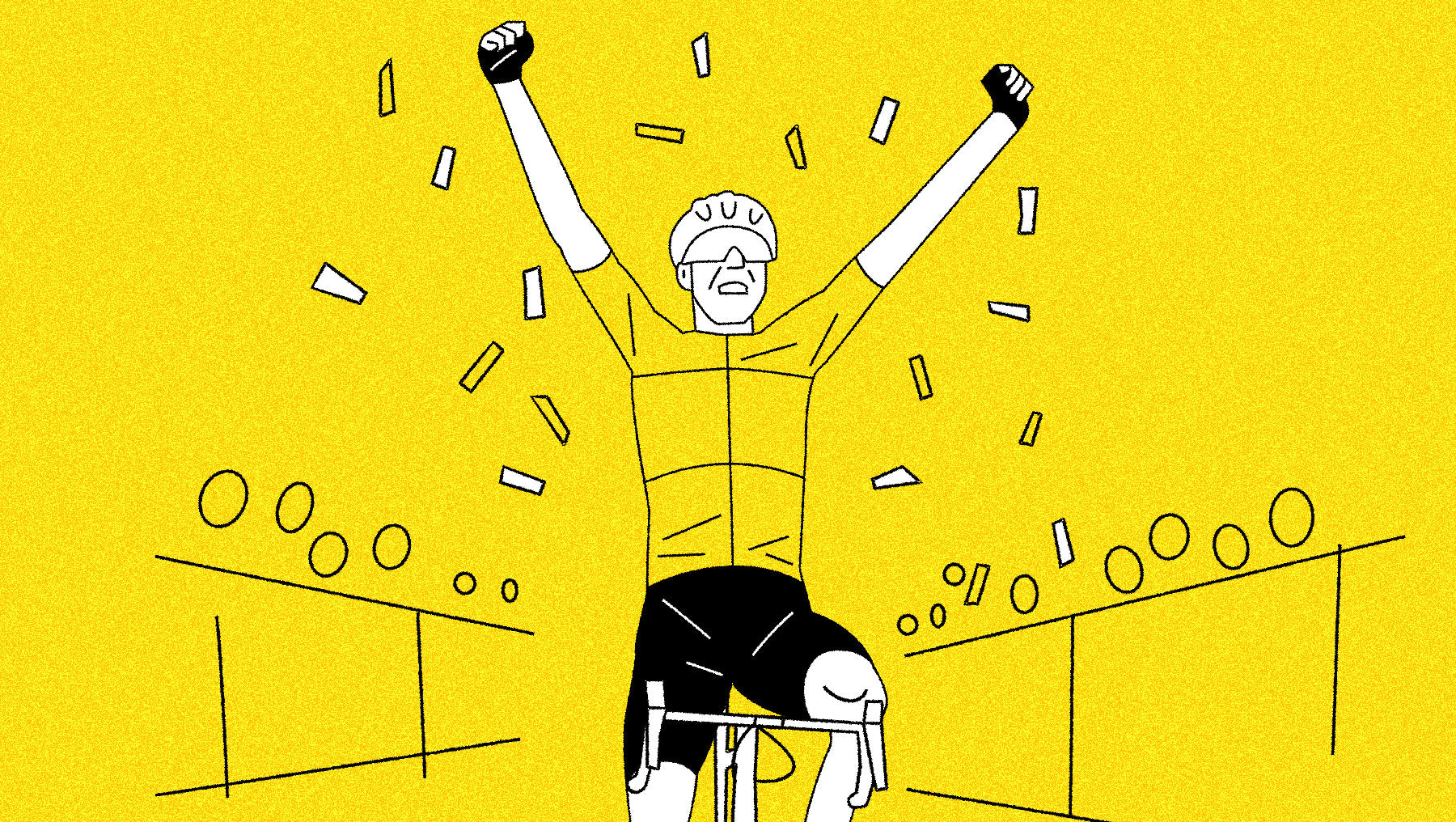

The Tour de France's yellow jersey is cycling's most prestigious award. The rider who wins it is typically an outstanding rider and a competent time-trialist.
The winner of the Tour de France is the rider who has the fastest time after all 21 stages. Every stage is timed from start to finish, and every second counts toward the race's General Classification (GC). Every day, the current leader of the race will wear the yellow jersey so they are easy to spot. The rider wearing the yellow jersey when the race reaches the last stage Paris is the winner.
Riders to watch: 2022 winner Jonas Vingegaard, 2020 & 2021 winner Tadej Pogačar, David Gaudu, Romain Bardet.
[newsletter]
Other Ways to "Win" at the Tour de France
The Yellow Jersey is the biggest prize, but there are multiple secondary prizes on offer too. Some teams and riders don’t even bother racing for the yellow jersey and instead focus on these prizes.
Just like the yellow jersey, each day, the current leader in each classification wears a special jersey color so they're easy to spot.
Points Classification - Green Jersey
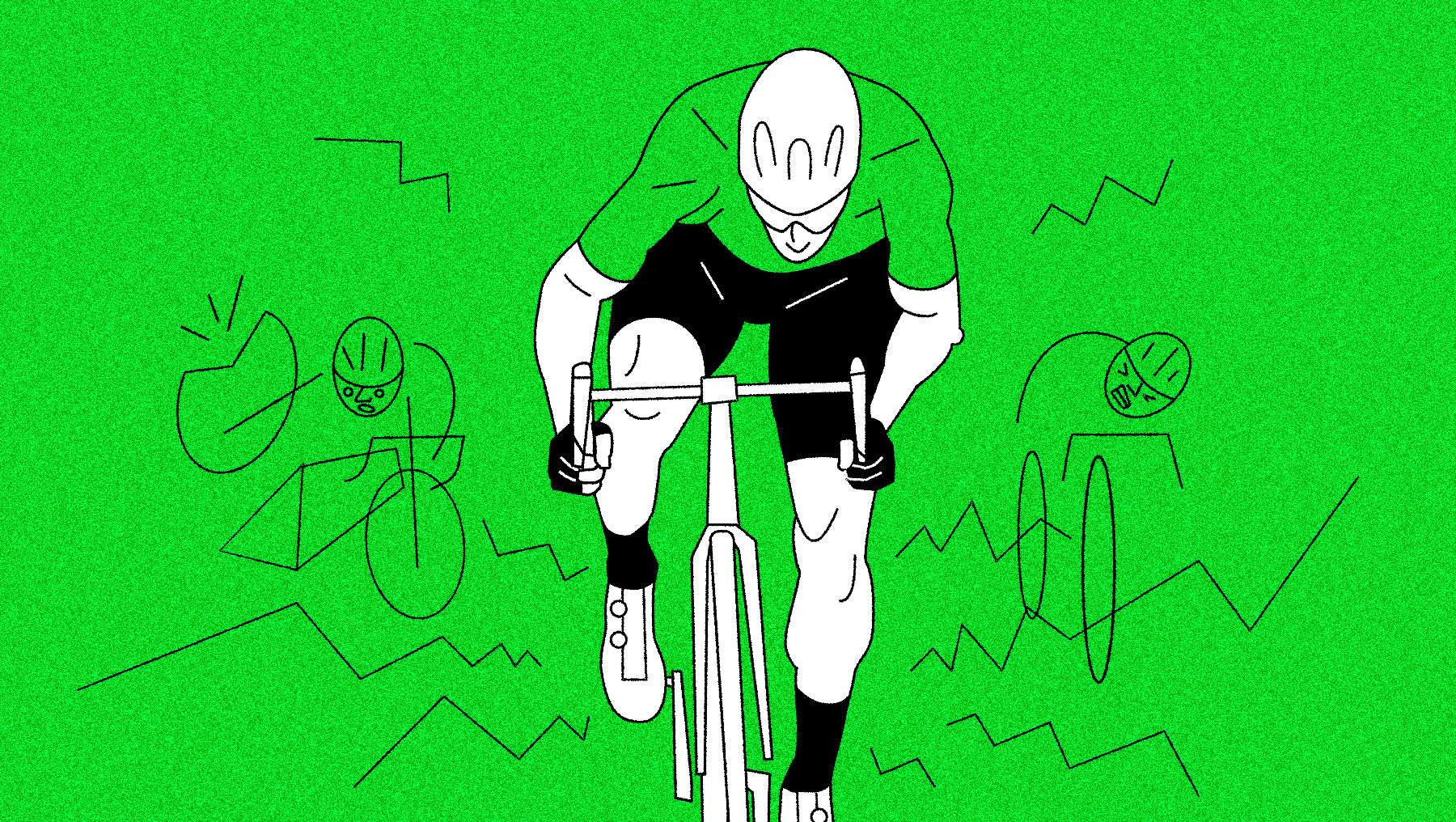

The sprinters own the road on flat stages, aiming to claim the green jersey as points classification leader. Peter Sagan is the only rider to win the prize seven times.
Also known as the sprinter’s jersey, this award goes to the rider who scores the most points throughout the race. Points are earned by finishing in the top-15 in a stage.
This classification favors “pure” sprinters (riders who don't compete on mountain stages), and more points are offered for winning flat stages. Riders can also earn points in mid-stage sprints that are usually stationed in towns to please the fans.
Riders to watch: Wout van Aert, Fabio Jakobsen, Jasper Philipsen, Mads Pedersen, and Dylan Groenewegen.
King Of The Mountains Classification - Polka-Dot Jersey
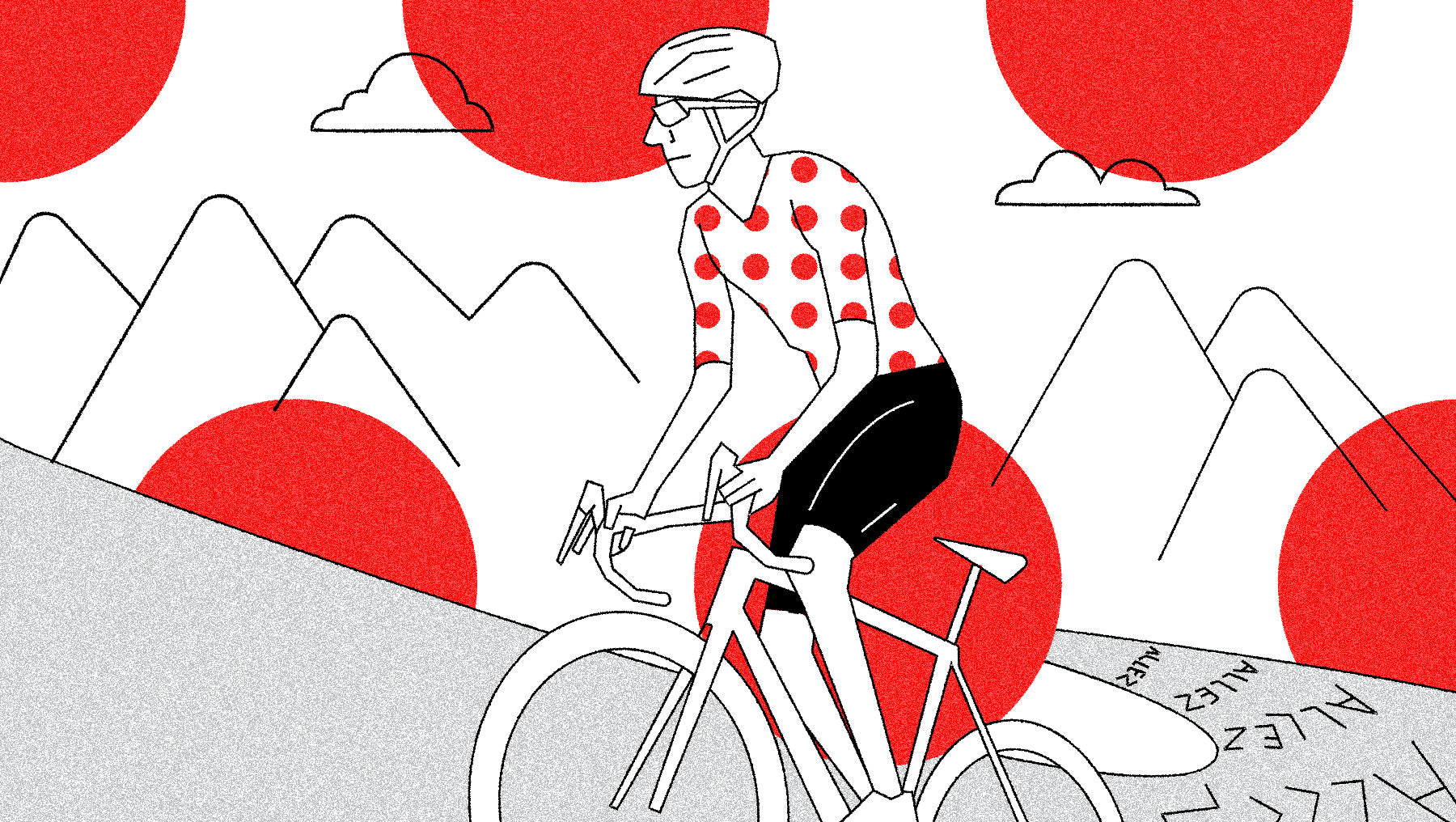

The King of the Mountains competition awards opportunistic climbers who escape in the Alps and Pyrenees and beat their rivals to the top of France's biggest climbs.
The Tour gives the polka-dot “King of the Mountains” jersey to the rider who collects the most points over the course of the race by reaching the summit of categorized climbs first.
The climb categorization system is opaque and subjective. What you need to know is that there are five climb categories. From easiest to hardest they are: category 4, category 3, category 2, category 1, and hors category (HC - French for “beyond categorization”). Riders get more points on harder climbs. Riders also get more points on mountaintop stage finishes, especially if they win.
Riders to watch: This one is tough to call until you reach the high mountains. Often anyone who’s in contention for the yellow jersey is a good bet.
Other Prizes
Can't hang with the world's best riders in the Tour's most difficult stages? Other awards are on offer for best young rider, best team, and most combative rider. It just depends on how you play your cards.
Best Young Rider Classification - White Jersey
This classification works the same way as the yellow jersey but is awarded to the highest-placed rider under 26 years of age. On rare occasions, a phenomenal young rider will win both the yellow and white jerseys.
Riders to watch: Tadej Pogačar, Jonas Vingegaard.
Best Team Classification - Yellow Helmets
Like the yellow or white jerseys, this award is given based on overall time in the race and the team with the lowest overall time wins this prize. Each team tabulates the finish times of its three best riders on every stage. The team leading this classification usually wears yellow helmets, helping them stand out in the bunch.
Most Aggressive Rider - Red Number
Also known as the Combativity Award, this is likely the most mysterious prize in the Tour. In every stage (except time trials), a jury decides which rider in the race was most aggressive — usually, that means attacking a lot or gambling on a breakaway. Late in the broadcast, the announcers usually note which rider was given the combativity prize. If you spot a rider with a red number on their jersey, then he was named most aggressive the stage prior. At the end of the Tour, one rider gets the Super Combativity award.
How Cycling Is Actually a Team Sport... Sort Of
Teamwork can be obvious like a paceline of riders sheltering their leader from a headwind, or it can be subtle like giving up a bottle or a gel to make sure the leader doesn't bonk. Either way, it's essential to succeed in the Tour.
Why are there teams if only one rider can win the Tour de France? Professional road cycling has a curious tension between the team and the individual. The key thing to remember is this: If a cyclist wins a stage or holds one of the leader’s jersey for a single stage, it is viewed as a team success.
So if only one rider “wins,” what do the other seven riders on the team do to contribute to this elusive concept of teamwork? Here are some ways a group of individual cyclists comes together as a team to support their leader:
- Getting into breakaways (small groups that attack off the front of the main group) — that way his team doesn’t have to work to chase the breakaway down.
- Chasing down breakaways — to give the leader a chance to win or place well.
- Retrieving food and water for the leader or other key riders — bottle service on the road … what could be more luxurious!
- Pacing the leader up key climbs — although drafting isn’t as crucial, it can be a psychological advantage to have a teammate at your side.
- Pacing the leader back to the peloton in the event of a crash, mechanical, or split in the group — without teammates to draft, it might be nearly impossible to rejoin the peloton on some fast-paced stages.
- Giving the leader their bike or a wheel in the event of a mechanical — this can often be quicker than waiting for a team car or neutral support to show up with a spare.
What Types of Riders Make Up a Team?
GC (general classification) riders - These are the riders vying for the Tour de France overall win. They need to be solid all-rounders who are good climbers and time trialists. They are usually the team leader and the rest of the team works to support them.
Sprinters - Sprinters don’t contend for the overall win, and are more interested in winning individual stages. They often wait to attack at intermediate sprints and the finish line of each stage. Some teams are built entirely around a sprinter and focus on winning stages or the green jersey.
Climbers - Climbing specialists excel at going uphill. Climbers compete for stage wins on the tough mountain stages or work to support their GC leader in the mountains.
Domestiques - Most riders on the team will work as “domestiques” to support their team leader. They allow their leader to draft behind them to conserve energy, pace them up climbs, carry food and water, and provide support in case of crashes or mechanicals.
Time Trialists - Some riders specialize in time trialing. They can compete for wins on time trial stages or work as powerful domestiques on flat and hilly stages
What Types of Stages Are in the Tour?
The Tour de France route is different every year. Each stage is unique and offers different challenges to the riders. Here are the types of stages riders will contend with over three weeks:
Flat Stages - Flat stages are the ideal hunting ground for sprinters. Teams with sprinters will often work to keep the peloton together on flat stages, to ensure it ends in a bunch sprint where their sprinter has the best chance of winning.
Hilly Stages - Hilly stages mix it up with rolling hills that make it more difficult for the peloton to stay together. These types of stages can be won by sprinters, climbers, or breakaway specialists.
Mountain Stages - This is often where the Tour de France is won and lost. Mountain stages climb up into the high mountains in the Alps and the Pyrenees and it's where GC contenders will fight to gain time on their rivals.
Time Trials - The Tour de France always features at least a couple of time trial stages. Riders set off individually to set the fastest time on a set course. With no riders to draft, it’s less about race tactics and more about pure speed and power.
Strategies and tactics
Yes, the Tour is a test of endurance, strength, and skill, but it's also a game that can be won or lost with the right strategies or tactics. The world's best teams pick the stages that suit their riders and try to strike at the perfect moment.
So we just covered some team dynamics, rider types, and stage types. How does it all fit together? Teams often settle on strategies prior to the race. They assess their strengths and weaknesses and find ways to succeed — whether that means winning the yellow jersey or simply wearing a King of the Mountains jersey for just one stage. Here are some examples of how teams might set their strategies, and how they might execute them with the right tactics:
Team with a top GC rider: Naturally, they’ll try to win the yellow jersey. This means surviving inconsequential flat and rolling stages to conserve energy for key mountain stages and individual time trials. The leader’s teammates will try to get into breakaways so that their team won’t spend energy chasing all day. They’ll also set up the team leader to attack on key climbs or at least follow his rivals to defend his position.
Team with top sprinter: To win the green jersey, they’ll target the flat stages. This means controlling the peloton and chasing down breakaways to set up a sprint finish. Like the GC team, they might also put a rider in the breakaway to ease the burden on the team, forcing rival sprint teams to chase. On mountain stages, the team might have to call riders back from the peloton to help pace their sprinter to the finish so he doesn’t get time-cut.
Team with top climber: Winning the King of the Mountains (KOM) classification is often less of an obvious team effort. These pretenders to the throne tend to be opportunistic. However, it is advantageous to have a teammate in the breakaway on a key mountain stage when points are up for grabs. Also, when defending the polka-dot jersey, teammates can contest the climbs and finish ahead of KOM rivals to spoil their attempt to take over the classification lead by scoring points.
Smaller team without top leader: These are the teams that always try to put a rider in the day’s breakaway. This could earn them the Combativity Prize, or if they play their cards right, a stint in a leader’s jersey or even a stage win. This strategy requires constant attacking in the early kilometers of the race — something most fans rarely see on the broadcast. It is a hectic, painful part of the stage, but it’s crucial in establishing a break. Meanwhile, a breakaway rider’s teammates might patrol the front of the peloton to disrupt the chase.
[button]Shop road bikes[/button]
Three Tips To Watch Like A Pro
 The Tour de France is a curious mix between nailbiting thrillers and snoozy days in the saddle. You never know what each stage will hold, but there are a few ways you can plan ahead to catch the action as a cycling fan.
The Tour de France is a curious mix between nailbiting thrillers and snoozy days in the saddle. You never know what each stage will hold, but there are a few ways you can plan ahead to catch the action as a cycling fan.
Now that you understand the basics of how the Tour de France is raced, what do you, the new cycling fan do? There are daily stages for three weeks. That’s a lot of cycling!
Even if you don't have a way to watch the TV broadcast, it's easy to find highlights and extended highlights on YouTube. Fortunately, you don’t have to put your life on hold to watch the Tour de France. There are some reliably important stages you can focus on to catch the key action.
Can’t watch daily? Pick the key mountain stages. There are usually about 5-8 key mountain stages when the overall race is won and lost. Most of them are summit finishes, and they’re split between France’s two key mountain ranges: the Alps and Pyrenees. The first few ordinarily come in stages 6-9 before the first rest day, and the second round is often scheduled for the final week of racing. Occasionally, another summit finish, such as Mont Ventoux in Provence, will be on the list of important stages.
Watching daily? Tune in when things really heat up. On most flat stages, you can wait until the final 20 kilometers to tune in and see the sprinters fight it out. Some rolling stages might be entertaining in the final 50-60 kilometers if late breakaways occur. On mountain stages, it’s best to start watching as early as possible because sometimes, crazy things happen on the day’s first climbs.
Watching a LOT of TDF? Look for the nuances. If you’re going to have the race on all day, every day, you’ll need to dig a little deeper to enjoy the subtleties of the race. Try keeping track of riders who are often making the breakaway. Watch the sprint teams work together — or not — to chase an escape. Who looks to have strength in numbers, and who is not present at the front of the race? Are the GC riders staying out of trouble or tail-gunning at the dangerous back of the peloton? Usually, at any given time in the race, any given rider is positioned where they are for a specific reason. Look for clues to sort out what is happening.
[button]Shop road bikes[/button]
More Fun Tour de France Info
[button]What Tour de France Racers Eat[/button]
[button]Guide to Netflix's Tour de France: Unchained[/button]
[button]The History of Innovative Tour de France Tech[/button]
[button]Our Best and Worst Moments of the 2022 Tour[/button]
[button]The Best Bikes of the Tour 2010-2019[/button]


















